Advantages And Disadvantages Of Serial And Parallel Data Transmission
четверг 28 марта admin 33
Slower serial data transmission is more compatible with such devices. Since the speed of serial transmission is more than adequate in such units, the advantages of low cost and simplicity of the signal interconnecting obtained. PARALLEL DATA TRANSMISSION line can be In a parallel data transmission system, each bit of the binary word to be transmitted must have its own data path. There are a variety of ways to implement this data path.
Data transmission is the transfer of data from point-to-point often represented as an electro-magnetic signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels, and storage media. T he term usually refers to digital communications (i.e.
Digital bit stream), but may include analog data transmission as well. Data transmission is a subset of the field of data communications, which also includes computer networking or computer communication applications and networking protocols, for example routing and switching. Parallel transmission is a method of transmitting data where each bit in a byte is transmitted in an individual channel or wire, hence multiple bits can be sent at the same time.
Parallel transmission is often used internally in a computer since it is quick and the distances involved are short, a s well as in devices such as disk drives, joysticks and a majority of printers. Parallel transmission, however, has the disadvantage of bits getting out or order when transmitted over a long distance.
Game ultraman fighting evolution 3 untuk pc matic. This is known as data skew.
Teach Any Computer Science Class We have put together a full GCSE Computer Science curriculum that will give you all the teaching materials you need to teach any topic. Whether you're a brand new Computer Science teacher, or you've been teaching ICT for years, our resources will save you hours and hours of lesson preparation every single week. There are two ways to transfer data between computers: Serial Transmission and Parallel Transmission.
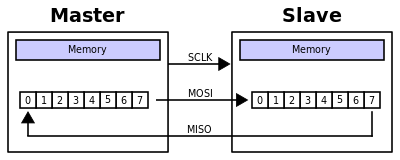
Serial Transmission Data is sent bit by bit from one computer to another in two directions. Each bit has a clock pulse rate.

Eight bits are transmitted at a time with a start and stop bit known as a parity bit, which is 0 and 1 respectively. Raspinovka razjyomov avtomagnitoli na nissan kashkaj. Data cables are used when transmitting data to a longer distance.
The data cable has D-shaped 9 pin cable that connects the data in series. Categories of Serial Transmission Asynchronous transmission – an extra bit is added to each byte to alert the receiver on the arrival of new data. 0 is used as a start bit while 1 used as a stop bit. Synchronous transmission – no extra bit is added to each byte. Data is transferred in batches which contains multiple bytes.
Parallel Transmission Several bits are transmitted together simultaneously with one clock pulse rate. It transmits quickly as it utilizes several input and output lines for sending the data. It uses a 25-pin port with 17 signal lines and 8 ground lines. The 17 signal lines are divided as • 4 lines – initiates handshaking • 5 lines – communicates and notifies errors • 8 lines – transfers data Applications Serial transmission occurs between two computers or from a computer to an external device located some distance away. Parallel transmission can take place within a computer system, through a computer bus or to an external device located a close distance away. Examples An example of serial mode transmission include connection between a computer and a modem using the RS-232 protocol.
An RS-232 cable can accommodate 25 wires, but only two of these wires are for data transmission, the rest are for overhead control signaling. The two data wires run on simple serial transmission in either direction. In this example, a computer may be far from the modem, making parallel transmission very expensive. With this, speed of transmission is considered less important compared to the economic advantage of serial transmission. An example of parallel mode transmission include connection between a computer and a printer. Most printers are within 6 meters or 20 feet from the transmitting computer and the slight cost for extra wires is offset by the added speed gained through parallel transmission of data. Comparison between Serial and Parallel Transmission Basis for Comparison Serial Transmission Parallel Transmission Definition Data flows in 2 directions, bit by bit Data flows in multiple directions, 8 bits (1 byte) at a time Cost Economical Expensive Number of bits transferred per clock pulse 1 bit 8 bits or 1 byte Speed Slow Fast Applications Used for long distance communication Used for short distance communication Example Computer to computer Computer to printer Differences between Serial and Parallel Transmission • Serial transmission requires a single line to send data.
Parallel transmission requires multiple lines to send data. • There are less errors and noise in serial transmission since transmission is done one bit at a time. There are more errors and noise in parallel transmission since transmission is done multiple bits at a time. • Serial transmission is slower since data flows through a single line.